India´s operational stock of industrial robots hit all time high.
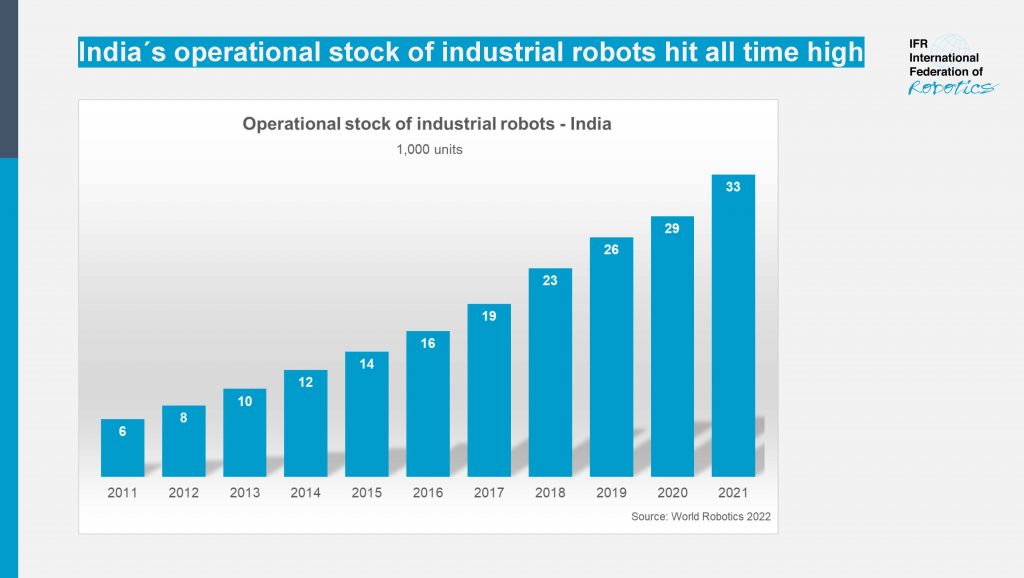
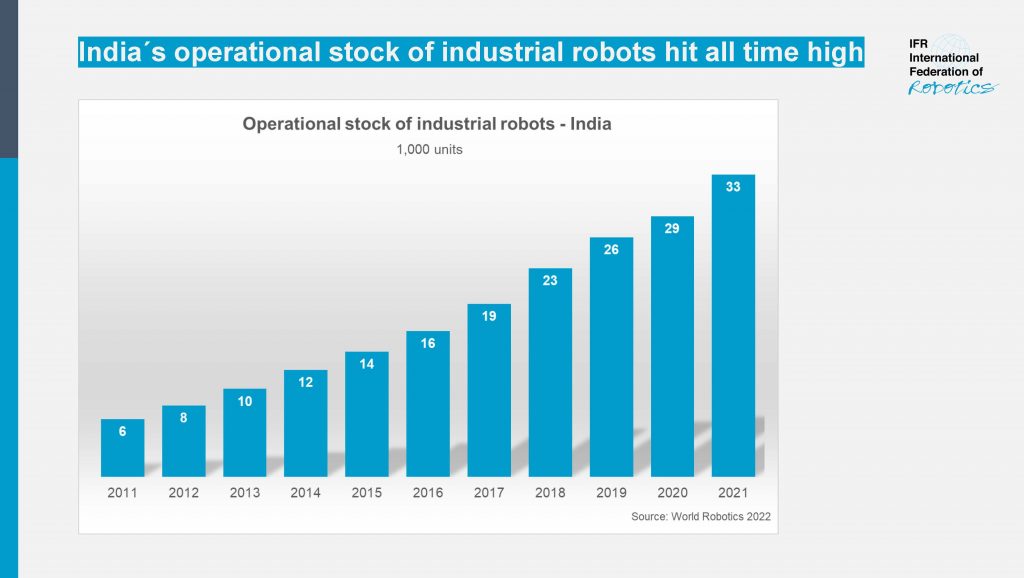
Sales of industrial robots in India reached a new record of 4,945 units installed. This is an increase of 54 percent compared to the previous year (2020: 3,215 units). In terms of annual installations, India now ranks in tenth position worldwide. These are findings of the report World Robotics, presented by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
“India is one of the world’s fastest-growing industrial economies,” says Marina Bill, President of the International Federation of Robotics. “Within five years, the operational stock of industrial robots has more than doubled, to reach 33,220 units in 2021. This corresponds to an average annual growth rate of 16% since 2016.”
Today, India is the world’s fifth largest economy measured by manufacturing output. According to World Bank data, India´s manufacturing value added in 2021 was USD 443.9 billion, a 21.6% increase from 2020.
The automotive industry remains the largest customer for the robotics industry in India with a share of 31% in 2021. Installations more than doubled to 1,547 units (+108%). The general industry in India is led by the metal industry with 308 units (-9%), the rubber and plastics industry with 246 units (+27%) and the electrical/electronics industry with 215 units (+98%).
Impressive potential for India
The long-term potential of robotics in India becomes clearer when compared to China: India´s robot density in the automotive industry, which is the number of industrial robots per 10,000 employees, reached 148 robots in 2021. China´s robot density hit 131 units in 2010 and skyrocketed to 772 units in 2021.
The Indian government supports growth in the industrial sector as one of the vital figures that affect the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Today, the country´s GDP of about USD 3 trillion ranks in fifth place, head-to-head with the UK and France – behind Germany, Japan, China and the USA – the International Monetary Fund reports.
Outlook for India
“As a result of the recent supply chain disruption, companies are rethinking their nearshoring strategies in Southeast Asia,” says Marina Bill. “India has traditionally been a popular destination for nearshoring in the manufacturing segment. The Indian government wants the country to be considered for new diversification options such as friendshoring, which is partnering with countries that share similar values and interests.”
The manufacturing sector is also expected to benefit from the government’s initiatives to boost its competitiveness and attractiveness for investors. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, for example, currently set to run until 2025, subsidizes companies that create production capacity in India in robot customer industries like automotive, metal, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Robots help to create new jobs
New manufacturing capacities in India are an important step to provide adequate education and employment opportunities for its people: According to projections of the United Nations, India now has a population of 1,4 billion, surpassing China for the first time. This means that India has a large and young workforce that can drive economic growth and innovation. India is expected to have the largest working-age population in the world by 2027.


International Federation of Robotics (IFR) connects the world of robotics around the globe. We aim at promoting the positive benefits of robots for productivity, competitiveness, economic growth and quality of work and life.